Industrial automation protocols are the backbone of communication between devices in modern industrial environments. These protocols facilitate seamless data exchange across a wide range of devices, such as PLCs, sensors, industrial switches, and controllers.
In this article, you’ll find the top 10 industrial automation protocols that power factory floors, data centers, and large-scale manufacturing systems, including Modbus, Profinet, Ethernet/IP, and others.
What is an Industrial Communication Protocol?
An industrial communication protocol defines the rules and standards that govern the transmission of data between devices in an industrial automation system. These protocols are critical for ensuring reliable, secure, and efficient communication within industrial environments.
Why Are Communication Protocols Important in Industrial Automation?
In industrial automation, communication protocols provide the foundation for device interoperability, real-time data transfer, and secure communication between machines and control systems. Whether you are working with Modbus serial protocol, Ethernet/IP industrial protocol, or any other standard, these protocols ensure that your devices work seamlessly together.
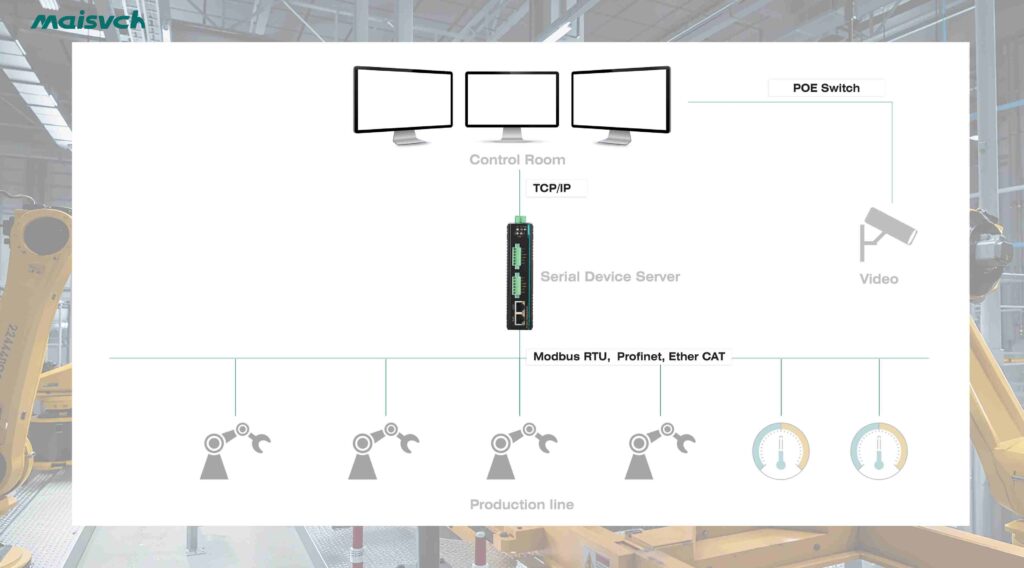
10 Most Common Communication Protocols in Industrial Automation Comparison
The table below compares communication type, speed, real-time capability and typical use cases across Modbus RTU/TCP, Ethernet/IP, PROFINET, HART, CAN bus, PROFIBUS, DeviceNet and BACnet.
Comparison of Industrial Communication Protocols
| Protocol | Communication Type | Speed | Real-Time Control | Common Use Case | Protocol Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Modbus RTU | Serial (RS485) | Low | No | Small to Medium Systems | Simplicity, Low Cost |
| Modbus TCP/IP | Ethernet | High | Yes | Large Scale Networks | High Speed, Large Networks |
| Ethernet/IP | Ethernet | High | Yes | Manufacturing, Real-Time Control | Real-time, High Speed |
| Profinet | Ethernet | High | Yes | Factory Automation, Real-Time | Real-time, Reliable |
| HART | Analog + Digital | Medium | Yes | Process Automation | Hybrid Communication |
| CAN Bus | CAN Bus | Medium | Yes | Automotive, Embedded | Real-time, Reliable |
| Profibus | Fieldbus | High | Yes | Automation | Fieldbus Protocol |
| DeviceNet | CAN Bus | Medium | Yes | Industrial Control | Flexible, Scalable |
| BACnet | Ethernet | Medium | Yes | Building Systems | Building Automation |
| Modbus Serial | Serial (RS232/RS485) | Low | No | Basic Systems | Simple, Low Cost |
1. Modbus RTU Communication Protocol
Modbus RTU is one of the oldest and most widely used communication protocols in industrial automation. It utilizes serial communication (RS485) for connecting devices such as PLCs, sensors, and HMIs. Despite its age, Modbus RTU remains a reliable choice for systems where simplicity and low-cost implementation are essential.
Advantages of Modbus RTU:
- Easy to implement and cost-effective.
- Supported by a wide range of devices.
- Works well in small to medium-scale industrial systems.
Key Use Cases:
- Industrial control systems.
- Remote monitoring of devices.
- SCADA systems integration.
For an in-depth understanding of how Modbus RTU works and its applications, read the comprehensive guide to Modbus RTU communication.
2. Modbus TCP/IP Communication Protocol
Modbus TCP/IP is an extension of Modbus RTU that works over Ethernet, making it faster and more suitable for larger networks. It is ideal for industries that require high-speed data transfer between multiple devices over a local area network (LAN).
Key Features of Modbus TCP/IP:
- Ethernet-based, offering higher speed and range.
- Compatible with modern industrial networks.
- Supports multiple devices in large-scale systems.
You can expand your network with our versatile Serial Servers, ensuring reliable data transfer over serial connections.
Why Choose Modbus TCP/IP?
If your system requires faster communication and supports Ethernet networks, Modbus TCP/IP is an excellent option, especially in industrial Ethernet protocols.
3. Ethernet/IP Protocol
Ethernet/IP (Ethernet Industrial Protocol) is a widely used industrial Ethernet protocol designed for real-time control and monitoring in manufacturing environments. It provides seamless data exchange between controllers, I/O devices, ethernet switches and other systems. It’s built on the standard Ethernet protocol, making it highly scalable and compatible with existing network infrastructure.
Benefits of Ethernet/IP:
- High-speed data transmission.
- Support for real-time control and monitoring.
- Seamless integration with existing Ethernet networks.
Industrial Ethernet Protocol Comparison
In comparison to Modbus TCP/IP, Ethernet/IP offers more robust features for complex industrial environments. For example, Ethernet/IP is specifically designed to handle large, real-time data transactions, making it a preferred choice in industries such as automotive manufacturing and process control.
4. Profinet Communication Protocol
Profinet is a powerful industrial Ethernet protocol commonly used in factory automation and process control. It provides fast and reliable communication for real-time data exchange and is widely adopted in Europe and beyond.
Profinet’s Features:
- Real-time data communication.
- High-speed connectivity for industrial control systems.
- Extensive support from Siemens and other major manufacturers.
Profinet vs. Modbus TCP/IP
While Modbus TCP/IP is widely used for basic industrial communication, Profinet provides more robust features for high-performance automation and real-time control.
5. HART Communication Protocol
HART (Highway Addressable Remote Transducer) is a hybrid protocol that combines analog and digital communication. It is widely used for process automation in industries such as oil and gas, chemicals, and water treatment.
Advantages of HART Protocol:
- Supports both analog and digital signals.
- Highly reliable for process control.
- Used in critical industries requiring high uptime.
6. CAN Bus Protocol
CAN Bus (Controller Area Network) is a multi-master protocol designed for real-time control in embedded systems. It is commonly used in automotive and industrial applications where real-time communication is crucial. Enhance your industrial automation system with CAN-Bus Converters for easy integration of different protocols.
Key Features:
- Real-time communication for embedded systems.
- Robust and reliable for automotive and industrial use.
- Cost-effective and flexible.
7. Profibus Protocol
Profibus (Process Field Bus) is a fieldbus protocol used in automation technology. It is known for its high reliability in transmitting data between devices such as sensors, actuators, and controllers.
8. DeviceNet Protocol
DeviceNet is another industrial network protocol that operates on the CAN Bus. DeviceNet is used primarily for connecting I/O devices to controllers in industrial automation systems. Although its popularity has waned in favor of newer Ethernet-based protocols, DeviceNet still finds use in legacy systems and offers reliable data exchange.
9. BACnet Protocol (Building Automation)
BACnet is a communication protocol designed for building automation systems. It is widely used in managing HVAC, lighting, and other building systems.
10. Modbus Serial Protocol
Although Modbus Serial (RS232/RS485) is one of the oldest communication protocols, it still serves a critical role in connecting devices that require simple, low-cost data exchange.
Other Types of Industrial Communication Protocols
OPC UA
OPC UA (Open Platform Communications Unified Architecture) is a flexible, platform-independent protocol designed for secure and reliable communication between machines. It plays a key role in communication protocols used in industrial automation, especially in connecting different devices and software for Industry 4.0 and IoT applications.
CANopen
CANopen is a communication protocol based on the CAN (Controller Area Network) standard. It is well-suited for real-time communication in embedded systems, automotive, and motion control applications. CANopen is simple, efficient, and reliable, making it a key player in industrial automation communication protocols.
CC-Link
CC-Link (Control & Communication Link) is widely used in Asia, especially in Japan. It is known for its high-speed, deterministic performance and ability to handle large networks of devices. CC-Link is popular in the automotive and manufacturing industries, offering reliable communication between machines and controllers.
For a more detailed list, refer to this Wikipedia page on automation protocols, such as for building automation, power-system automation, automatic meter reading, and vehicular automation.

FAQs on Industrial Automation Communication Protocols
1. What is an Industrial Communication Protocol?
An industrial communication protocol defines the rules for data exchange between devices in industrial systems, ensuring seamless integration and reliable communication.
2. What Are the 7 Network Protocols?
Some of the most common industrial network protocols include Modbus, Ethernet/IP, Profinet, HART, DeviceNet, CAN Bus, and BACnet.
3. What Are the Most Common OT Protocols?
In the context of operational technology (OT), the most common protocols include Modbus RTU, Ethernet/IP, and Profinet.
4. What is the Most Popular Industrial Communication Protocol?
The Modbus TCP/IP protocol remains one of the most popular communication protocols used in industrial applications due to its wide compatibility and reliability.
5. What is the Purpose of a Communication Protocol?
The purpose of a communication protocol is to ensure data integrity, secure transmission, and interoperability between different industrial devices in automated systems.
6. What Are Some Examples of Communication Protocols?
Examples of common communication protocols include Modbus RTU, Ethernet/IP, Profinet, and HART.
Conclusion: Which Protocol is Best for Your Application?
Choosing the right industrial communication protocol depends on various factors such as network size, device compatibility, speed requirements, and reliability. While some protocols like PROFINET and EtherNet/IP dominate factory automation, others like OPC UA and HART are gaining traction in Industry 4.0 and process automation.



